Categories
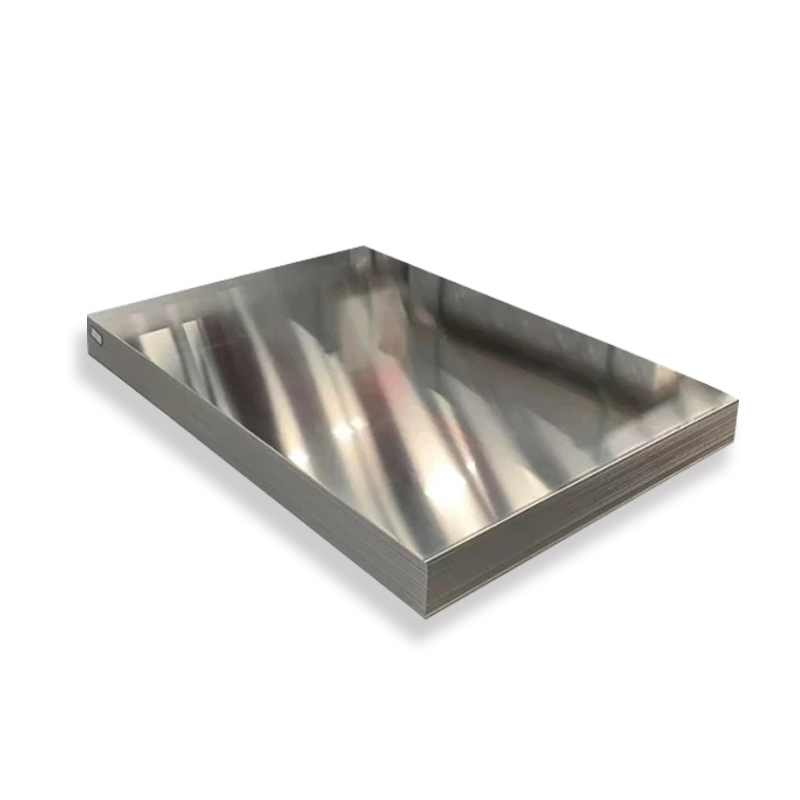
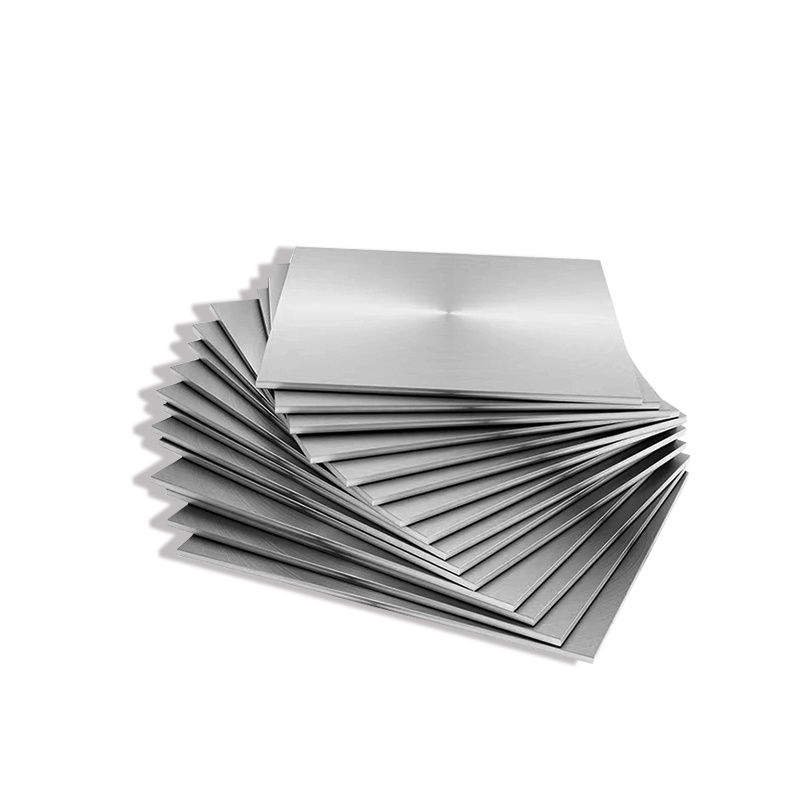
Product
304 stainless steel is a superior material with regard to corrosion resistance, heat resistance, low temperature strength and mechanical properties, as one of the most widely used types of stainless steel. In addition, it has exceptional hot-workability such as stamping and bending, without leaving heat treatment hardening phenomenon.
304L stainless steel is remarkably similar to 304 stainless steel in their chemical composition with one key difference. the maximum carbon of 304L stainless steel content is set at 0.08%, whereas grade 304L stainless steel has a maximum carbon content of 0.03%. This is why the “L” in 304L can be interpreted as extra-low carbon. It is widely used in the production of equipment and parts that demand better corrosion resistance and formability.
310S stainless steel is austenitic chromium-nickel stainless steel, with good oxidation resistance, corrosion resistance, because of a higher percentage of chromium and nickel, so that it has much better creep strength, with good high temperature resistance.
316 stainless steel also contains 2-3% molybdenum, in addition to iron, chromium and nickel. The addition of molybdenum significantly improves the performance of 316 stainless steel in certain corrosive environments, especially those containing chlorides. 316 stainless steel is more commonly used in situations requiring higher corrosion resistance.
316L stainless steel features a lower proportion of carbon in its composition. The amount of carbon cannot be higher 0.03%. This lowers the risk of carbon precipitation, making it a better option for welding to achieve maximum corrosion resistance.
304 stainless steel is a highly-recognized material for its corrosion resistance, heat resistance, low temperature strength and mechanical properties. In addition, it has exceptional hot-workability such as stamping and bending, without leaving heat treatment hardening phenomenon, being one of the most widely used types of stainless steel.
304L stainless steel has a very similar chemical composition to 304 stainless steel with one key difference. The maximum carbon content is set at 0.08% for 304, whereas grade 304L stainless steel has a maximum carbon content of 0.03%. It is more often adopted in the production of equipment and parts that require better corrosion resistance.
310S stainless steel is austenitic chromium-nickel stainless steel, with good oxidation resistance, corrosion resistance, because of a higher percentage of chromium and nickel, it has better creep strength, can work at high temperatures continuously, with good high temperature resistance.
316L stainless steel has a lower proportion of carbon in its composition, the amount of carbon cannot go over 0.03%. This lowers the chance of carbon precipitation, making it an ideal option for welding to ensure maximum corrosion resistance.
316 stainless steel contains 2-3% molybdenum, aside from iron, chromium and nickel. The addition of molybdenum significantly improves the performance of 316 stainless steel in certain corrosive environments, especially those containing chlorides. 316 stainless steel is more commonly used when higher corrosion resistance is needed.
304 stainless steel, as one of the most commonly used types of stainless steel, is an outstanding material when it comes to corrosion resistance, heat resistance, low temperature strength and mechanical properties. In addition, it has exceptional hot-workability so it leaves no heat treatment hardening phenomenon.
Similar to 304 stainless steel, 304L stainless steel has one key difference in its chemical composition. The maximum carbon content of 304 stainless steel is 0.08%, whereas grade 304L stainless steel has a maximum carbon of only 0.03%. This is why the “L” in 304L can be interpreted as extra-low carbon. It is usually used to produce equipment and parts that demand better corrosion resistance and formability.
316 stainless steel has extra 2-3% molybdenum, in addition to iron, chromium and nickel. Molybdenum significantly leads to better performance of 316 stainless steel in certain corrosive environments containing chlorides. So it is a very common choice in situations requiring higher corrosion resistance.
316L stainless steel, similar to 316 stainless steel, has a lower amount of carbon of no more than 0.03% in its composition. This is meant to reduce the risk of carbon precipitation, to make a better choice for welding to achieve maximum corrosion resistance.
304 stainless steel highly stands out in terms of corrosion resistance, heat resistance, low temperature strength and mechanical properties, being one of the most widely used types of stainless steel. In addition, it has exceptional hot-workability such as stamping and bending, without leaving heat treatment hardening phenomenon.
304L stainless steel is remarkably similar to 304 stainless steel in their chemical composition. but there is one key difference. In grade 304 stainless steel, the maximum carbon content is set at 0.08%, whereas grade 304L stainless steel has a maximum carbon content of 0.03%. This is why the “L” in 304L can be interpreted as extra-low carbon. It is widely used in the production of equipment and parts that require better corrosion resistance and formability.
316 stainless steel also contains 2-3% molybdenum, in addition to iron, chromium and nickel. The addition of molybdenum significantly improves the performance of 316 stainless steel in certain corrosive environments, especially those containing chlorides. 316 stainless steel is more commonly used in situations requiring higher corrosion resistance.
316L stainless steel has a lower proportion of carbon in its composition. To qualify as 316L stainless steel, the amount of carbon cannot exceed 0.03%. This decreases the risk of carbon precipitation, making it a better option for welding to ensure maximum corrosion resistance.